1. Fedi P, Bafico A, Soria AN, Burgess WH, Miki T, Bottaro DP, et al. Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of the Human Dkk-1 Homologue, a Novel Inhibitor of Mammalian Wnt Signaling. J Biol Chem (1999) 274(27):19465–72. 10.1074/jbc.274.27.19465
2. Hameed A, Brady JJ, Dowling P, Clynes M, O’Gorman P. Bone Disease in Multiple Myeloma: Pathophysiology and Management. Cancer Growth Metastasis (2014) 7:33–42. 10.4137/CGM.S16817
3.Pinzone JJ, Hall BM, Thudi
NK, Vonau M, Qiang YW, Rosol TJ, et al. The Role of Dickkopf-1 in Bone
Development, Homeostasis, and Disease. Blood (2009) 113(3):517–25. 10.1182/blood-2008-03-145169
DKK-1
is a 266-amino acid protein with an approximate molecular mass of 26-kDa, and
it possesses six secondary structures, which are two alpha helices and four
β-sheets. It has the colipase-like fold in C-terminal Cys domain, which likely
allows it to serve as an interactive surface. DKK-1 expression appears to be
preferential in some adult tissues including bone, placenta, prostate, spleen,
and colon. DKK-1 has been shown to play an important role as a Wnt signaling
pathway antagonist in several studies. DKK-1 is down-regulated in human colon
tumours; hence, it may act as a tumour suppressor. High DKK-1 expression
indicated favourable responses to chemotherapy in brain tumours whereas;
over-expression of DKK-1 was found in human hepatoblastomas, Wilms’ tumours and
multiple myelomas. Moreover, since overexpression of DKK-1 in osteoblasts
causes osteopenia, it is also regarded as a negative regulator of normal bone
homeostasis.
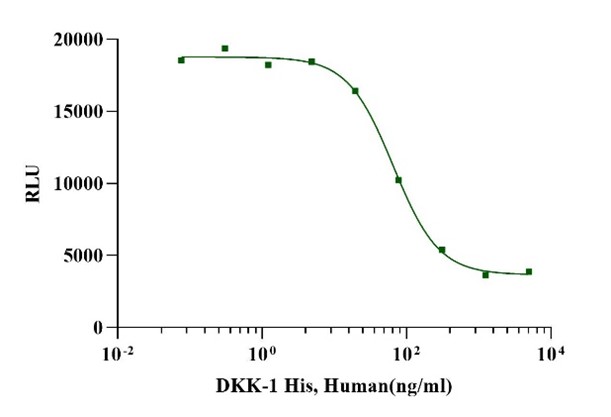
Measured
by its ability to inhibit Wnt induced TCF reporter activity in HEK293T human
embryonic kidney cells. Recombinant Human DKK-1 His Tag inhibits a constant
dose of 50 ng/ml of Recombinant Human Wnt‑Surrogate. The EC50 for this effect is less than
60 ng/ml.
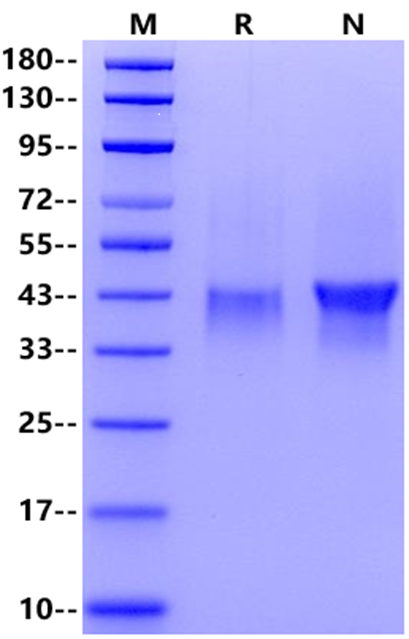
1μg
(R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).