18kDa (Reducing)
1. Immunol Rev. 2018 Jan;281(1):154-168.
2. Cytokine. 2022 Sep:157:155961. Epub 2022 Jul 14.
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) is a tissue-derived nuclear cytokine from the IL-1 family abundantly expressed in endothelial cells, epithelial cells and fibroblast-like cells, both during homeostasis and inflammation. It functions as an alarm signal (alarmin) released upon cell injury or tissue damage to alert immune cells expressing the ST2 receptor (IL-1RL1). The major targets of IL-33 in vivo are tissue-resident immune cells such as mast cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) and regulatory T cells (Tregs). Other cellular targets include T helper 2 (Th2) cells, eosinophils, basophils, dendritic cells, Th1 cells, CD8+ T cells, NK cells, iNKT cells, B cells, neutrophils and macrophages. IL-33 exhibits pleiotropic function in inflammatory diseases and particularly in cancer. IL-33 may play a dual role as both a pro-tumorigenic and anti-tumorigenic cytokine, dependent on tumor and cellular context, expression levels, bioactivity and the nature of the inflammatory environment
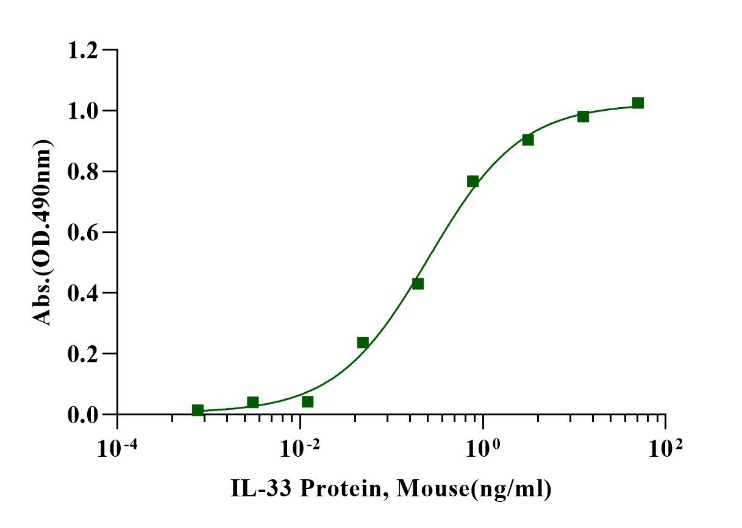
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using D10.G4.1 mouse helper T cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 0.3ng/ml.
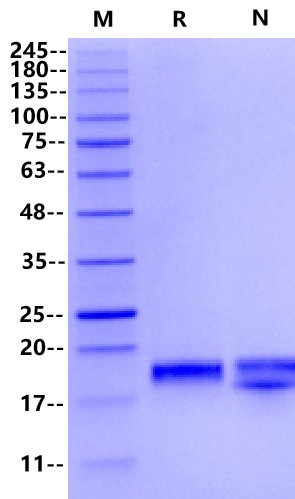
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).