26 kDa (Reducing)
20mM Tris-HCl, 200 mM NaCl, 2mM CaCl2, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.4 @ 25°C
Store at -25 ~ -15℃ for 2 years
1. Melicherová, Kristína,Krahulec, Ján,?afránek, Martin,et al.Optimization of the fermentation and downstream processes for human enterokinase production in Pichia pastoris[J].Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2017, 101(5):1927-1934.
2. Gasparian M E , Ostapchenko V G , Schulga A A ,et al.Expression, purification, and characterization of human enteropeptidase catalytic subunit in Escherichia coli[J].Protein Expression & Purification, 2003, 31(1):133-139.
Enterokinase is a specific protease that cleaves after lysine at its cleavage site Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp-Lys. It will sometimes cleave at other basic residues, depending on the conformation of the protein substrate. This product is a high-purity, high-specific activity enterokinase prepared using a recombinant E.coli. It boasts a broad range of applicability (operating temperature: 4-45°C; pH range: 4.5-9.5) and retains partial activity in the presence of various detergents and denaturants.
5 U/μl hEK, 20mM Tris-HCl, 200 mM NaCl, 2mM CaCl2, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.4 @ 25°C
Optimal incubation times and enzyme concentrations must be determined empirically for a particular substrate. Typical reaction conditions are as follows:
1、Combine 500 ug of sample with reaction buffer *(Recommended Reaction Buffer: 20 mM Tris-HCl, 50 mM NaCl, 2 mM CaCl2 (pH 8.0))
2、Add 1 U of Enterokinase,
3、Incubate at 25°C for 16 hours
Enterokinase is inhibited by high salt concentrations. For optimal activity NaCl concentration should be 50mM or less. The pH of the buffer should be between 6 and 9. The enzyme requires 2 mM Calcium for activity.
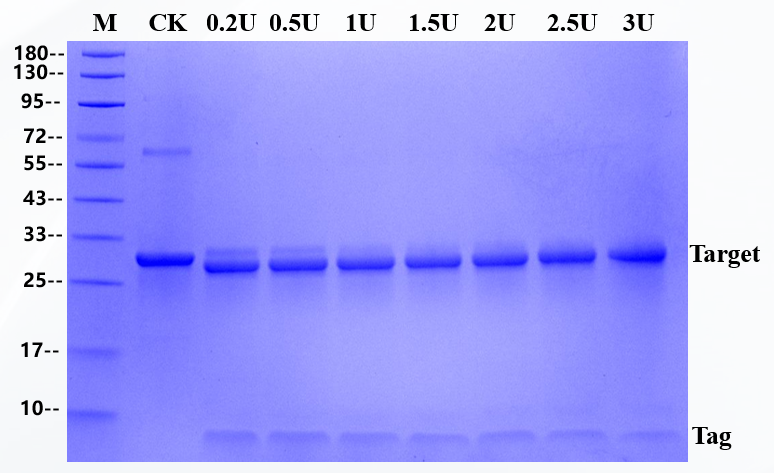
The substrate of 500μg fusion protein was digested by enzyme, and the addition amount of enterokinase in the sample was 0.2U, 0.5U, 1U,1.5U, 2U,2.5U and 3U respectively. The substrate is a fusion protein with a molecular weight of 30.5 KD and reacted at 25 ℃ for 16 hours, and the target band of 27.6kD is produced after restriction enzyme digestion.
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).