45 kDa (Reducing)
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1. Kim KA, Zhao J, Andarmani S, et al. R-Spondin proteins: a novel link to beta-catenin activation. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(1):23-26.
2. de Lau W, Barker N, Low TY, et al. Lgr5 homologues associate with Wnt receptors and mediate R-spondin signalling. Nature. 2011;476(7360):293-297.
R-spondin3 is a member of the R-spondin family of secreted proteins that play crucial roles in regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. R-spondin3 is known to enhance Wnt signaling by binding to the LGR4-6 receptors, leading to the stabilization of the Wnt receptor complex and promoting the nuclear translocation of β-catenin. This results in the activation of Wnt target genes involved in various cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and stem cell maintenance. R-spondin3 has been implicated in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and regeneration, as well as in the pathogenesis of certain diseases, including cancer.
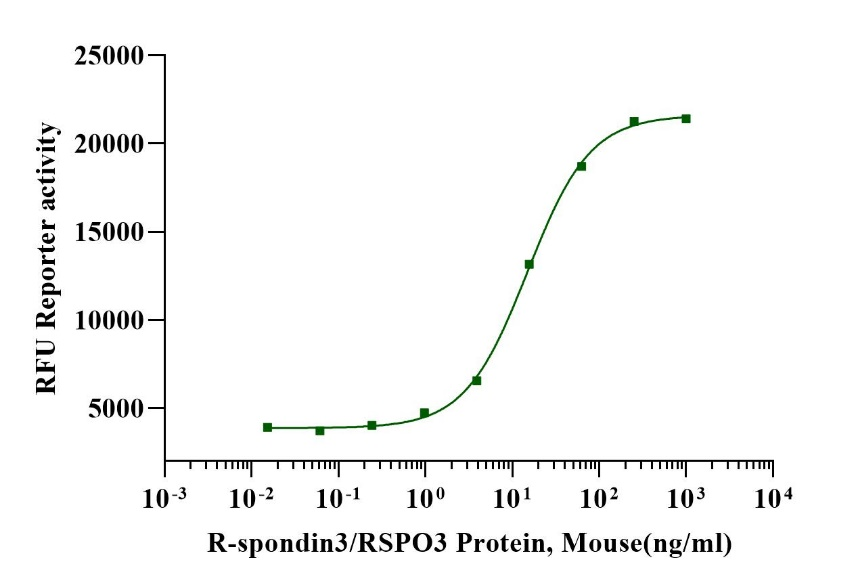
Measured by its ability to induce Topflash reporter activity in HEK293T human embryonic kidney cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 20ng/mL in the presence of 5ng/mL Recombinant Human Wnt‑3a.
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. When Recombinant Mouse RNF43 mFC Chimera, is immobilized 2µg/mL (100 µl/well), Recombinant Mouse R-spondin3/RSPO3 His Tag binds with an EC50 of 0.02-0.036μg/ml.