38-50kDa (Reducing)
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1.Greenwald, R.J. et al. (2005) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23:515.
2.Bour-Jordan, H. et al. (2011) Immunol. Rev. 241:180.
CD86, also known as B-lymphocyte activation antigen B7-2 (formerly referred to as B70), is a member of the cell surface immunoglobulin superfamily. Predominantly existing as a monomer on cell surfaces, B7-2 interacts with two co-stimulatory receptors: CD28 and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4), which are expressed on T cells. This interaction initiates signal pathways that regulate T cell activation and tolerance, cytokine production, and the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). B7 family members are transmembrane cell surface molecules that play crucial roles in immune activation and the maintenance of immune tolerance.
B7-2 is highly expressed on activated antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as B cells, dendritic cells, and monocytes, as well as on vascular endothelial cells. B7-2 and its closely related counterpart, B7-1/CD80, exhibit overlapping yet distinct functional characteristics.
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
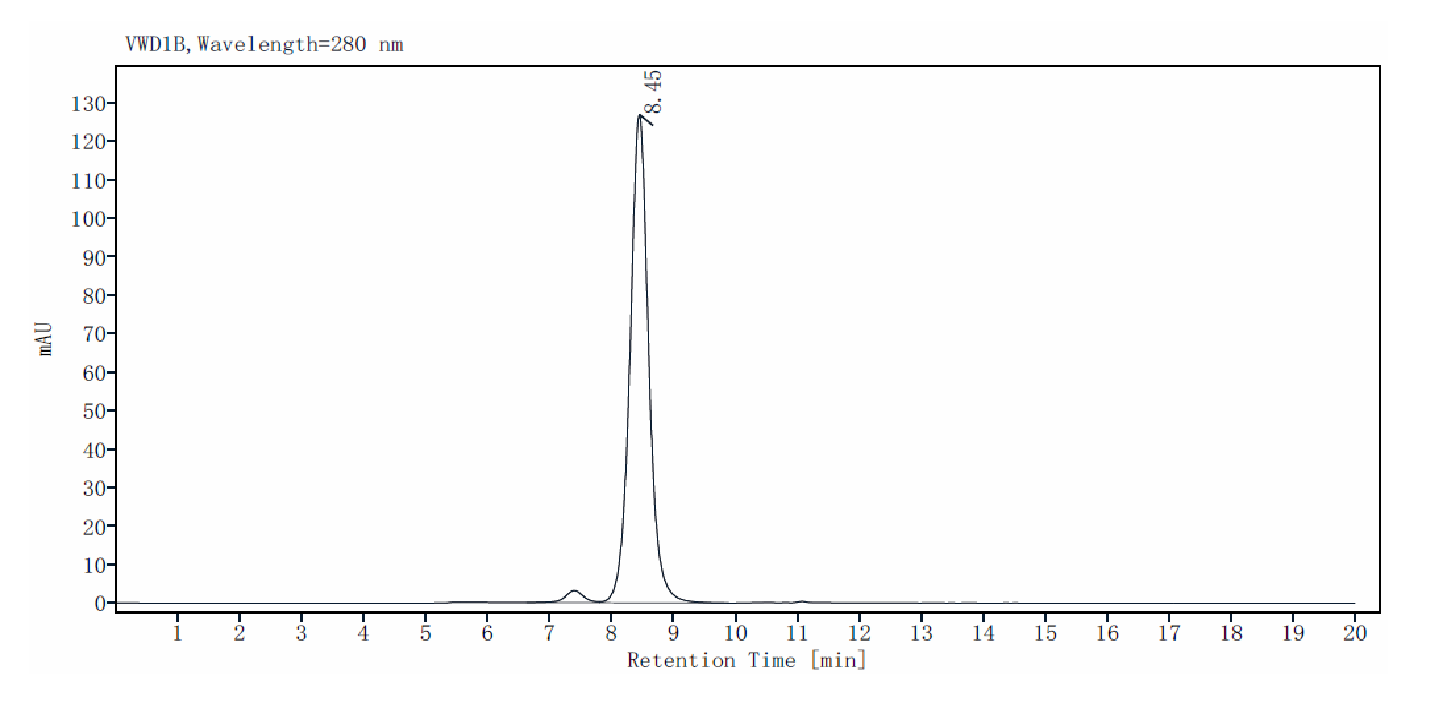
The purity of B7-2/CD86 His Tag Protein,Mouse is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC.
Immobilized B7-2/CD86 His Tag Protein, Mouse (Cat. No. UA011072) at 2.0μg/mL (100μL/well) can bind CTLA-4/CD152 Fc Chimera Protein, Mouse (Cat. No. UA010773) with EC50 of 46.98-90.08ng/mL.