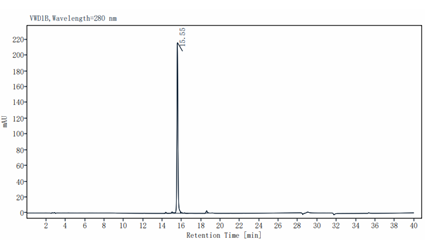
1. Van Damme J, Rampart M, Conings R, et al. 1990. Eur J Immunol. 20:2113-8.1/2.
IL-8(Interleukin-8) is one of the first discovered chemokines and belongs to the CXCL family, in which the first two conserved cysteines are separated by one residue. In vivo, IL-8 exists in two forms: a 77-amino acid protein produced by endothelial cells, and the more active 72- amino acid protein produced by monocytes. IL-8 is often associated with inflammation, it has been cited as a proinflammatory mediator in gingivitis and psoriasis. The functions of IL-8 are to induce rapid changes in cell morphology, activate integrins, and release the granule contents of neutrophils. Thus, IL-8 can enhance the antimicrobial actions of defense cells. It is secreted by monocytes, macrophages and endothelial cells. IL-8 signals through CXCR1 and CXCR2 to chemoattract neutrophils, basophils, and T cells. IL-8 is also a potent promoter of angiogenesis.

Measured by human U-87 MG cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 10ng/ml.
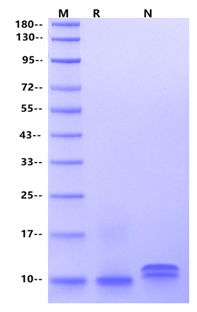
1μg(R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).