72-94KDa (Reducing)
>95% by SDS-PAGE
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1.Matsumoto K, et al. (2010) Soluble adhesion molecule E-selectin predicts cardiovascular events in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 59(3): 320-4.
2.Stancanelli B, et al. (2010) Soluble e-selectin is an inverse and independent predictor of left ventricular wall thickness in end-stage renal disease patients. Nephron Clin Pract. 114(1): c74-80.
E-selectin, also known as endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) and CD62E, is an inducible adhesion molecule that is expressed on the surfaces of stimulated vascular endothelial cells and is sometimes implicated in cancer cell metastasis. It has a complex mosaic structure that includes a large extracellular region with a lectin domain, an EGF-like domain, and a short consensus repeat (SCR) domain. This is followed by a transmembrane region and a relatively short (32 amino acid) cytoplasmic tail. As part of the LEC-CAM or selectin family, E-selectin recognizes and binds to sialylated carbohydrates, including those from the Lewis X and Lewis A families, which are found on monocytes, granulocytes, and T-lymphocytes. It facilitates the rolling and stable arrest of leukocytes on activated vascular endothelium. Additionally, E-selectin is suggested to transduce activating stimuli via the MAPK signaling cascade during leukocyte adhesion.
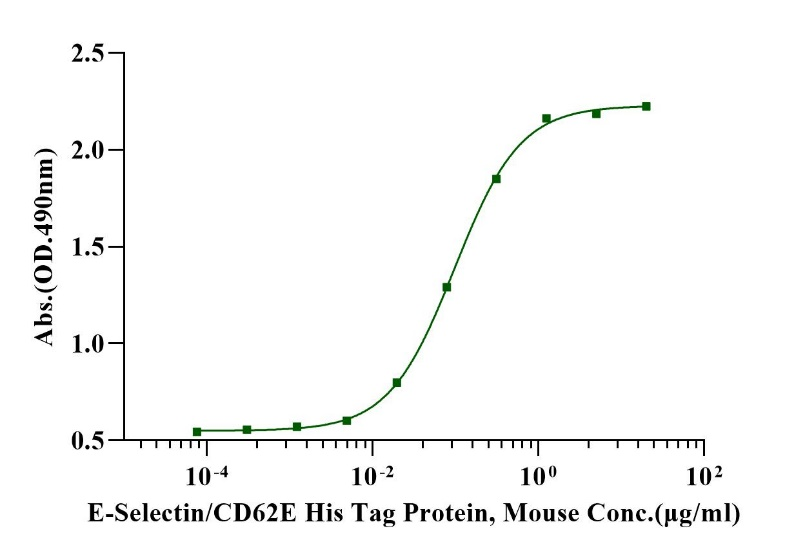
Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. The EC50 for this effect is less than 100 ng/ml.
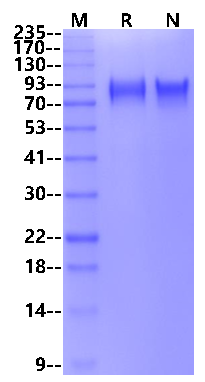
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).

The purity of E-Selectin/CD62E His Tag Protein, Mouse is more than 95% determined by SEC-HPLC.