25-40kDa (Reducing)
Reconstitute at 0.1-1 mg/ml according to the size in ultrapure water after rapid centrifugation.
1.Melero I, et al. (2008) Multi-layered action mechanisms of CD137 (4-1BB)-targeted immunotherapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29(8): 383-90. Thum E, et al. (2009) CD137, implications in immunity and potential for therapy. Front Biosci. 14: 4173-88.
CD137 (also known as 4-1BB) is a surface co-stimulatory glycoprotein originally described as present on activated T lymphocytes, which belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. CD137 can be expressed by activated T cells, but to a larger extent on CD8 than on CD4 T cells. In addition, CD137 expression is found on dendritic cells, follicular dendritic cells, natural killer cells, granulocytes and cells of blood vessel walls at sites of inflammation. The best characterized activity of CD137 is its costimulatory activity for activated T cells. 4-1BB signaling either by binding to 4-1BBL or by antibody ligation delivers signals for T-cell activation and growth, as well as monocyte proliferation and B-cell survival, and plays an important role in the amplification of T cell-mediated immune responses.
2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
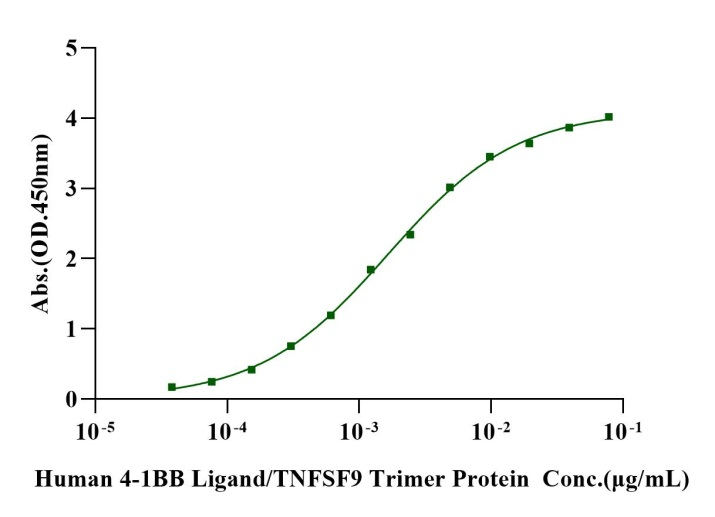
Immobilized Biotinylated 4-1BB/TNFRSF9 His&Avi Tag Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010943) at 2 μg/mL on Streptavidin precoated (0.5μg/well) plate, can bind Human 4-1BB Ligand/TNFSF9 Trimer Protein with EC50 of 1.47-1.85ng/ml.

Immobilized Biotinylated 4-1BB/TNFRSF9 His&Avi Tag Protein, Human (Cat. No. UA010943) at 2 μg/mL on Streptavidin precoated (0.5μg/well) plate, can bind V6 Anti-Human CD137 Monoclonal Antibody with EC50 of 24.57-31.20ng/ml.