1. Li Zhou. (2021) Adv Exp Med Biol. 21:191-210.
The IL-36 family belongs to a larger IL-1 superfamily and consists of three agonists (IL-36α/β/γ), one antagonist (IL-36Ra), one cognate receptor (IL-36R) and one accessory protein (IL-1RAcP). The receptor activation follows a two-step mechanism in that the agonist first binds to IL-36R and the resulting binary complex recruits IL-1RAcP. Assembled ternary complex brings together intracellular TIR domains of receptors which activate downstream NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Antagonist IL-36Ra inhibits the signaling by binding to IL-36R and preventing recruitment of IL-1RAcP.
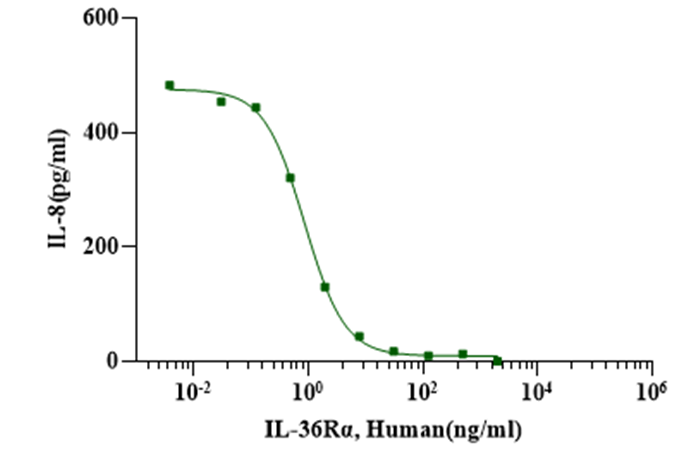
Measured by its ability to inhibit IL-36β induced IL-8 secretion in A431 human epithelial carcinoma cells. The ED50 for this effect is less than 1μg/mL in the presence of 10ng/mL of recombinant human IL-36β.

2μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).

>95% as determined by RP-HPLC.