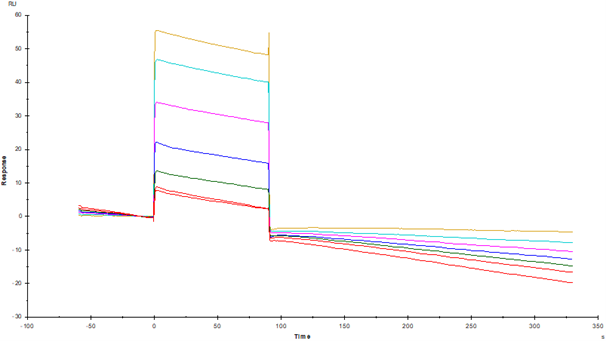
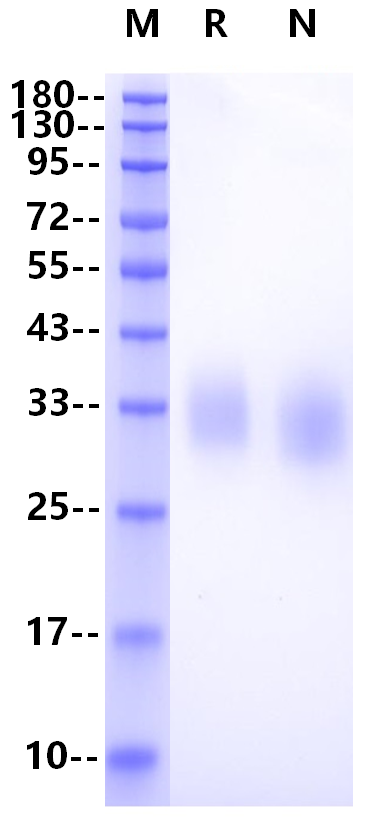
IgG Fc receptor (Fc γ R) is a member of the Ig superfamily, which plays a role in activating or inhibiting immune response. Human Fc γ Rs is identified as three types: RI (CD64), RII (CD32) and RIII (CD16) can produce multiple subtypes. There are 3 Fc γ RII / CD32 genes (A, B and C) in human, 2 genes in monkeys (A and B) and one Fc γ RII B in mice. Mature Fc γ RIIA is a type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein. About 40 kDa is composed of extracellular domain, transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic domain, and the extracellular domain includes two IgG domains. Monkey Fc γ RIIA protein has 89% homology with human Fc γ RIIA. CD32a is expressed in a variety of immune cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, platelets, etc., and initiates inflammatory responses during ligand binding, including cytolysis, phagocytosis, degranulation and production of cytokines. This response can be regulated by co-expression of inhibitory receptors such as CD32B, and the intensity of the signal depends on the proportion of activated and inhibitory receptors.