Davidson D. et al. (2005) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 18 signals through FGF receptor 3 to promote chondrogenesis. J Biol Chem. 280(21): 20509-15.
Liu Z. et al. (2007) FGF18 is required for early chondrocyte proliferation, hypertrophy and vascular invasion of the growth plate. Dev Biol. 302(1): 80-91.
Fibroblast Growth Factor 18 (FGF-18) plays an important role in skeletal development and bone homeostasis. Mature human FGF-18 shares 99% amino acid sequence identity with mouse and rat FGF-18. It is expressed in embryonic somites and the neural fold, adult lung, cerebellar and hippocampal neurons, hair follicle root sheath cells, and osteogenic mesenchymal cells. FGF-18 is a heparin-binding growth factor that belongs to the FGF family. Proteins of this family play a central role during prenatal development, postnatal growth and regeneration of a variety of tissues, by promoting cellular proliferation and differentiation. FGF-18 is required for normal skeletal development. Recombinant Human FGF-18 derived from E.coli is a 20 kDa protein consisting of 173 amino acid residues, resulting from C-terminal truncation of the full length protein.
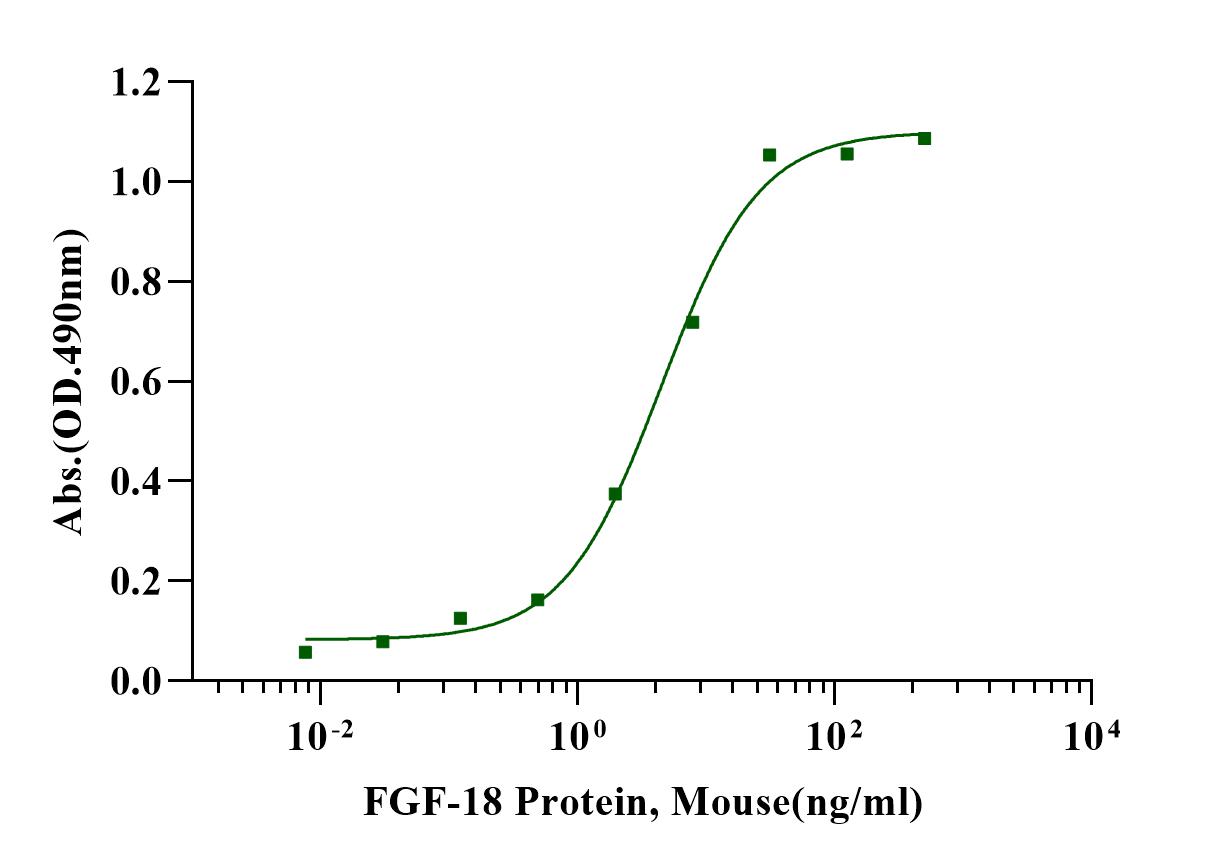
Measured in a cell proliferation assay using Balb/c3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. The EC50 this effect is less than 6ng/ml in the presence of 10μg/ml heparin.
1μg (R: reducing condition, N: non-reducing condition).
>95% as determined by RP-HPLC.